Apolobamba Mountain Range – Puno
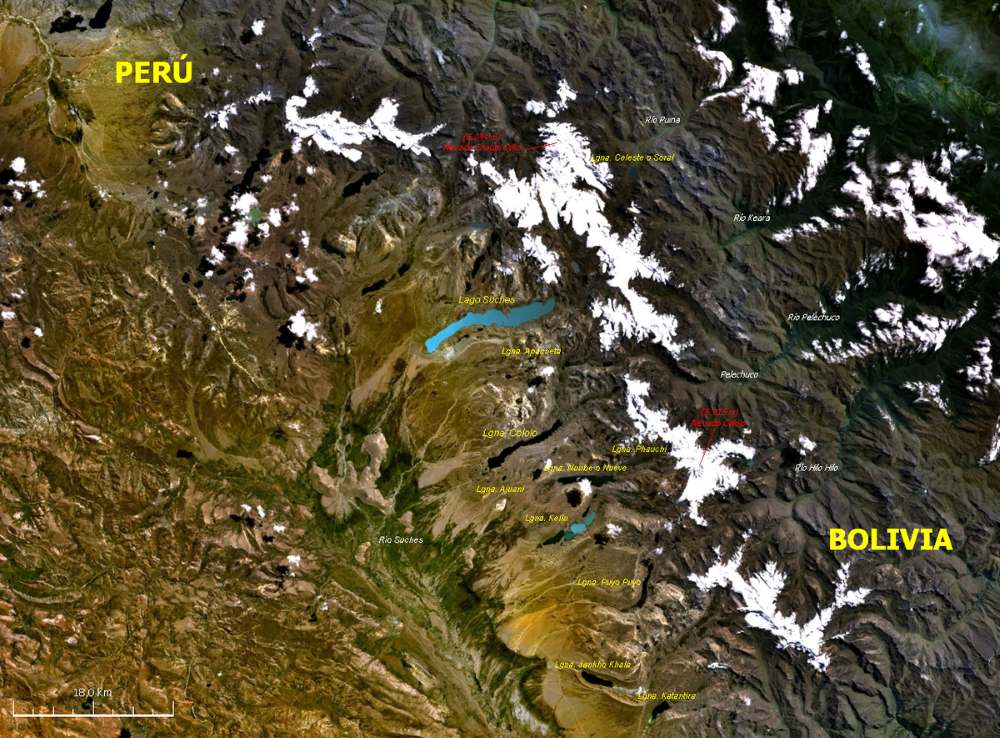
The Apolobamba | Puno mountain range is an impressive mountain range located on the border between Bolivia and Peru. This mountain range extends for approximately 180 kilometers and is part of the Andes, one of the most important mountain ranges in the world.
The Cordillera Apolobamba is known for its scenic beauty, with snow-capped peaks, crystalline lagoons and rich biodiversity. This area is home to numerous species of flora and fauna, including some endangered animals such as the spectacled bear and the vicuña.
In addition to its ecological value, the Cordillera Apolobamba also has cultural and spiritual importance for the local communities, who have inhabited this region for centuries. Many of these communities still preserve their traditions and traditional lifestyles, and some practice agriculture on Andean terraces.
The Cordillera Apolobamba offers opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, trekking, climbing and wildlife observation. It is also a popular destination for cultural tourism, where visitors can learn about the region’s rich history and culture while exploring its picturesque villages and archeological sites.
location
The Apolobamba Mountain Range is located in the Andean region of South America, on the border between Bolivia and Peru. It extends for approximately 180 kilometers and encompasses part of the Puno region of Peru and a portion of the Bolivian departments of La Paz and Beni.
To be more specific, the range is located north of Lake Titicaca and southeast of the city of La Paz in Bolivia. In Peru, it is located south of the city of Puno and west of the Madre de Dios River. This strategic location makes it an attraction for both tourists visiting Peru and those touring Bolivia in search of breathtaking scenery and outdoor adventure.
How to get there?
Traveling to the region: If you are in Bolivia, the common starting point is usually the city of La Paz. From there, you can take a bus or hire a private transport service to the area near the Cordillera Apolobamba. In Peru, the city of Puno is a common starting point.
Accessing nearby communities: The Apolobamba Range is close to several local communities. From nearby cities, you can take other transportation, such as cabs or shared vans, to reach the villages closest to the mountain range. These towns can serve as starting points to explore the region.
Hire local guides: Once in the communities near the mountain range, it is advisable to hire local guides who know the area and can lead you safely through the trails and trekking routes. They can also provide you with valuable information about the local culture and history of the region.
Trekking or hiking: Depending on your interests and abilities, you can choose from a variety of outdoor activities, such as hiking, trekking or climbing. Local guides can help you plan routes and activities that suit your preferences and level of experience.
It is important to research and plan ahead for your trip to the Cordillera Apolobamba, as it is a remote and mountainous area that can present logistical challenges. It is also essential to respect local regulations and follow safety guidelines during your stay in the region.
What does Apolobamba mean?
The name “Apolobamba” is of Andean origin and has diverse meanings according to cultural interpretation. In Andean cosmology, “Apolobamba” may be related to local deities or divinities. The word could derive from “Apu”, which in Quechua means “lord” or “divinity”, and “lloqta” which translates as “village”, so “Apolobamba” could be interpreted as “village of the gods” or “sacred place of the gods”.
Another possible interpretation is that “Apolobamba” comes from the word “Apurubamba”, which in Quechua means “sacred river”. This could refer to the importance of water in the region, as rivers and streams are vital for life and agriculture in the Andean mountains.
In general, the name “Apolobamba” evokes a sense of sacredness and spiritual connection with the land and nature, reflecting the rich Andean cosmovision that survives in the region.
history
The history of the Cordillera Apolobamba is deeply rooted in the rich cultural tradition of the indigenous communities that have inhabited this region for millennia. Although there are no accurate written records of its history, it is believed that indigenous populations, such as the Aymara and Quechua, have inhabited these mountains since pre-Columbian times.
During the Inca period, the Apolobamba Mountains were part of the vast Inca empire, and the Incas considered these mountains sacred and divine. The Incas built roads and established settlements in the highlands of the Andes, including the Apolobamba region.
With the arrival of the Spanish and the conquest of the Inca empire in the 16th century, the region underwent significant changes in its social, economic and cultural structure. The Spanish imposed new forms of organization and religion, but many of the indigenous traditions and beliefs persisted, adapting to the new circumstances.
In more recent times, the Cordillera Apolobamba has witnessed several historical events and political changes, especially in the context of Bolivia and Peru. The region has been the scene of social movements and struggles for the rights of indigenous communities, as well as conflicts related to land and natural resources.
Today, the Cordillera Apolobamba is valued as much for its cultural and spiritual importance as for its stunning natural beauty. It is a popular destination for ecotourism and adventure tourism, where visitors can experience life in the Andean mountains and learn about the region’s rich history and culture.
Recommendations:
Research and plan: Before traveling, research the Cordillera Apolobamba, including trekking routes, weather conditions and services available in the area. Plan your itinerary in advance and consider hiring local guides if necessary.
Prepare your equipment: Be sure to bring appropriate outdoor gear, such as sturdy hiking boots, warm and waterproof clothing, camping equipment, maps and compass or GPS, as well as basic first aid supplies.
Respect for nature and culture: Respect the natural and cultural environment of the Cordillera Apolobamba. Do not leave garbage, do not damage the flora and fauna, and respect the traditions and customs of the local communities.
Safety first: Prioritize your safety at all times. Pay attention to the terrain conditions, avoid taking unnecessary risks and follow the indications of the local guides. Also, be aware of changing weather conditions and possible high altitudes.
Adaptación a la altitud: Si planeas realizar actividades a gran altitud, como trekking en la Cordillera Apolobamba, tómate el tiempo necesario para adaptarte gradualmente a la altitud antes de emprender rutas más exigentes. Bebe suficiente agua, descansa adecuadamente y escucha tu cuerpo en todo momento.
Apoyo a las comunidades locales: Considera apoyar a las comunidades locales comprando productos locales, utilizando servicios de guías locales y respetando las regulaciones establecidas para el turismo en la zona. Tu contribución ayuda a fortalecer la economía local y a preservar las tradiciones culturales de la región.
Siguiendo estas recomendaciones, podrás disfrutar de una experiencia segura, enriquecedora y respetuosa en la Cordillera Apolobamba, mientras te sumerges en la belleza natural y cultural de esta impresionante región de los Andes.











